Academic Lublin in numbers:
- nearly 60 thousand students
- 9 universities, including 5 public and 4 private
- over 200 fields of study at public and private universities
- nearly 9 000 international students from over 100 countries
- over 15 thousand graduates each year.
In terms of the number of students, Lublin is one of Poland’s leading academic centers and the largest in the eastern part of the country. There are five public and four private universities here, distinguished not only by the largest number of students in the Lubelskie Voivodeship but also by their scientific and research achievements, appreciated in the country and abroad.
Tab. 1. The total number of students in the 2023/2024 academic year
| Public universities | The total number of students in the 2023/2024 academic year |
| Maria Curie-Sklodowska University | over 15,5 thousand |
| The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin | over 7,6 thousand |
| Lublin University of Technology | over 6,7 thousand |
| The University of Life Sciences in Lublin | over 6 thousand |
| The Medical University of Lublin | nearly 7 thousand |
| Private universities | |
| WSEI University | over 8 thousand |
| Vincent Pol University in Lublin | nearly 3 thousand |
| The University College of Enterprise and Administration in Lublin | over 2 thousand |
| Higher School of Social Sciences in Lublin | over 1 thousand |
Source: Compiled by the Lublin City Office based on data obtained from universities – December 2023.
Owing to the comfort of living in the city and a high standard of education, students readily choose Lublin. Universities annually expand and modernize their infrastructure and research facilities, supports the scientific and non-scientific activity of students and undertake activities aimed at graduates. Despite a student decline tendency in the country, resulting mainly from the population decrease, the number of students in Lublin has remained at a similar level. In Lublin, there are nearly 60 000 students in total, including nearly 9 thousand international students and 500 Erasmus+ students.
Tab. 2. The degree of internationalization of Lublin universities in 2010/11-2023/24
| Academic year | Overall | Including foreign students | Percentage of foreign students |
| 2023/24 | 57 370 | 8 788 | 15,32% |
| 2022/23 | 58 196 | 9 014 | 15,50% |
| 2021/22 | 59 135 | 8 154 | 13,80% |
| 2020/21 | 60 364 | 7 305 | 12,00% |
| 2019/20 | 60 315 | 6 707 | 11,12% |
| 2018/19 | 60 988 | 6 352 | 10,42% |
| 2017/18 | 62 977 | 6 272 | 9,96% |
| 2016/17 | 64 330 | 6 172 | 9,59% |
| 2015/16 | 67 315 | 5 662 | 8,41% |
| 2014/15 | 69 658 | 4 474 | 6,42% |
| 2013/14 | 71 913 | 3 082 | 4,29% |
| 2012/13 | 77 173 | 2 385 | 3,09% |
| 2011/12 | 80 839 | 1 764 | 2,18% |
| 2010/11 | 84 221 | 1 432 | 1,70% |
Source: In-house study based on data provided by Local Data Bank GUS, VII 2024
Lublin universities
- Public:
| Maria Curie-Skłodowska University in Lublin | https://www.umcs.pl/ |
| The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin | https://www.kul.pl/ |
| Lublin University of Technology | http://www.pollub.pl/ |
| The University of Life Sciences in Lublin | https://www.up.lublin.pl/ |
| The Medical University of Lublin | https://www.umlub.pl/ |
- Private:
| WSEI University | https://www.wsei.lublin.pl/ |
| Vincent Pol University in Lublin | https://wssp.edu.pl/ |
| The University College of Enterprise and Administration | https://wspa.pl/ |
| Higher School of Social Sciences in Lublin | https://www.wsns.lublin.pl/ |
MARIA CURIE-SKłODOWSKA UNIVERSITY IN LUBLIN
Maria Curie-Skłodowska University in Lublin is the largest higher education institution in Eastern Poland. It has 12 faculties in Lublin plus the UMCS branch campus in Puławy. The university offers over 90 programs taught in Polish or English and more than 300 specializations available to choose from.
Campus
Most university facilities, including Rectory, Main Library, and Center of Physical Culture, are gathered in Lublin’s center. UMCS disposes of 2600 housing options in 9 on-campus residence halls. Comfortable accommodation in university residence halls suits a variety of budgets and needs of students.
University of chances
Every year UMCS educates over 16 000 students, including 1700 foreigners. They have numerous opportunities to improve their foreign language proficiency, develop artistically, and participate in sports activities. The university also offers them a variety of certified training courses available free of charge and the possibility to participate in international internships to over 180 partner universities from all over the world.
All students can join numerous organizations and science clubs. Multimedia Center of Art and Culture lets them develop an artistic passion. The Academic Sports Association of Maria Curie-Skłodowska University (AZS UMCS Lublin) is open to everybody who wants to improve his athletic skills.
Graduate’s career
Maria Curie-Skłodowska University takes care of its students’ future. Study programs are designed to meet the labor market demands and make opportunities to establish cooperation with prospective employees. Moreover, the university offers professional educational counseling and career guidance to every student who needs practical tips.
CONTACT
Pl. M. Curie-Skłodowskiej 5
20-031 Lublin
https://www.umcs.pl/
Phone: +48 (81) 537 51 00
ADMISSIONS
Pl. Marii Curie-Skłodowskiej 5
20-031 Lublin
https://irk.umcs.lublin.pl/
Phone: +48 (81) 537 58 80
E-mail: rekrutacja@umcs.pl rekrutacja.ua@umcs.pl rekrutacja.ru@umcs.pl
International Student Office
Phone: +48 (81) 537 29 26
E-mail: studyinenglish@umcs.pl
THE JOHN PAUL II CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN LUBLIN
The John Paul II Catholic University in Lublin is the oldest higher education institution in the city. Since the year of foundation in 1918, the university has been well-known and appreciated worldwide. KUL offers its students a full range of courses — from humanities to science and a fantastic studying atmosphere.
Campus
There are two campuses of Catholic University in Lublin and another one in Stalowa Wola. The main campus is situated in the city center, where the student life prospers all day and night. Campus ‘Poczekajka’ with faculty buildings, residence halls, and academic sports center is located 4 km apart from the main campus. Still, it is well-connected to the city center by numerous bus lines.
Multifaceted development
KUL is a resilient research center in many fields — theology, philosophy and humanities, law, medicine and science. The best lecturers passionately share their knowledge with students and watch over them, keeping in mind the university’s superior values.
KUL offers bachelor’s, master and Ph.D. studies as well as postgraduate studies. There are more and more courses in English and international agreements with foreign partner universities. Students can take the TELC exam or certification exams in other languages (Italian, Spanish, French, or Chinese) in the university examination center.
One of the advantages of KUL is eventful academic life. Students can develop their hobbies by joining one of almost fifty science, artistic, or sports clubs.
University for everyone
The university is based on catholic values but still open to everyone regardless of his nationality or religious identity. There are hundreds of KUL’s international students who enjoy the freedom of convictions and great atmosphere, and a high level of education.
KUL takes care of students with disabilities. KUL CAN was created to help them in everyday activities at the university — they organize transport, unique books and devices, and financial support. The buildings are fully equipped with the necessary facilities. Moreover, there are scholarships dedicated to not well-off students.
Students of KUL often point out individual approaches and exceptional relations with lecturers as the university’s main advantages. They can rely on their colleagues and share their ideas in student clubs.
CONTACT
al. Racławickie 14
20-950 Lublin
http://www.kul.pl/
Phone +48 (81) 445 41 01
ADMISSIONS
Collegium Norwidianum p. CN-004 (parter)
Al. Racławickie 14
20-950 Lublin
http://kandydat.kul.pl/
Phone: +48 (81) 445 41 37, +48 (81) 445 42 16
E-mail: rekrutacja@kul.pl, study@kul.pl
LUBLIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Lublin University of Technology has over 70 years of tradition and experience in university-level technical education. Having established its market position, the university educates students on 6 faculties, over 30 programs.
Campus and staff
The campus of LUT is centralized – all faculty buildings, residence halls, dining halls, health centers, and sports facilities are situated close to each other. There are convenient bus lines that connect the campus to other districts of Lublin. It takes just ten minutes walking to the city center.
Lublin University of Technology cares about the high level of education. That is why labs and classrooms are equipped with modern and cutting-edge technical devices. Also, the academic staff is highly-qualified and supportive of every single student.
University for students
LUT does its best to create graduate profiles matching available careers. Practical programs of studies make students sure of their professional future and numerous opportunities for university training and career advice.
Young people from all over the world are welcome to LUT. They can study in English and take Polish language courses. The university takes care of students with disabilities and not well-off students by offering them extensive financial support.
Student’s life
The campus of LUT is full of pubs and restaurants, so the student’s life is on day and night. Young people can join student organizations and clubs, numerous sports teams, or academic student societies.
The university encourages its students to participate in international student exchange and internship programs. Moreover, it offers international English language certificate exams.
CONTACT
ul. Nadbystrzycka 38 D
20 – 618 Lublin
http://www.pollub.pl/
Phone: +48 (81) 538 41 40
E-mail: politechnika@pollub.pl
ADMISSIONS
Studies in English:
Office of International Education
Str Nadbystrzycka 42a, room 9,
20-501 Lublin, Poland
E-mail: lut.international@pollub.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 538 4703,4357
Fax. +48 (81) 538 4772
http://en.pollub.pl
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF LUBLIN
The Medical University of Lublin has a long history of conducting medical studies in Poland and almost 30 years of experience teaching international students. Over 2000 students have graduated from the English Division, developed a Dentistry Program, and several Medicine Programs designed for students worldwide during the following years.
University’s mission
Combining tradition and modernity, Medical University of Lublin is developing competent staff of medical professions based on research and didactic resources. Concerned about the quality and competitiveness of education, MUL participates in the ongoing changes of the education market. The university raises public awareness in the field of medical and health sciences and informs about the need of continuous development and the use of scientific achievements of everyday life.
International licenses
Over 2000 students from two dozen different countries and over 2000 graduates can approve the MUL’s high level of education.
Professional training programs run by the Medical University of Lublin are based on EU standards. UN approves courses, Medical Board of New York and California, National Accreditation Committee, the University Commission on the Quality of Medical Education and other countries – Saudi Arabia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Graduates of MUL can take medical licensing examinations in other EU countries and the US, Canada, New Zealand, Australia, and more. There is also USMLE and NBME practice exam center at the university.
University of possibilities
MUL has long been a participant in the Erasmus+ programs accessible for all students. Moreover, dozens of academic associations show that young people can learn more about a field of studies or develop their hobbies – academic choir, student clubs, and sports teams.
tudy at MUL is much more affordable than in other cities. All students can apply to get a place in the university’s residence halls.
CONTACT
al. Racławickie 1
20-059 Lublin
www.umlub.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 448 50 00
E-mail: kancelaria@umlub.pl
ADMISSIONS
Collegium Novum, p. 11 i 12
al. Racławickie 1
20-059 Lublin
http://www.rekrutacja.umlub.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 448 50 73, +48 (81) 448 50 70
E-mail: rekrutacja@umlub.pl
UNIVERSITY OF LIFE SCIENCE IN LUBLIN
The University of Life Science in Lublin has educated in fields of agriculture, biotechnology, and science. Its students particularly appreciate an individual approach presented by high-qualified teaching staff and practical programs of studying.
Campus
he campus of the University of Life Science in Lublin is situated close to the academic city, where are numerous restaurants, pubs, and intellectual culture buildings. All didactic facilities are fully equipped with modern devices. Residence halls provide accommodation in fully furnished bedrooms with shared bathrooms and a shared TV room, study room, gym, and canteen.
Investing in the future, the university has a program of continuous investment and improvement on campus. Key projects include the Investment-Implementation of New Technologies in Agricultural Engineering Centre and a new building for the University Library.
Practical programs
With a strong emphasis on practical application, well-equipped laboratories, and modern teaching methods, the University of Life Science in Lublin guarantees the highest education level. Practical training and internships in Poland and abroad are a mandatory part of the study process.
Students also have almost unlimited access to many scientific sources. The Central Library’s collection includes approximately 380 000 books, scientific periodicals, and unique items. Through PCs connected to the university servers, the library, being a participant in numerous consortia of scientific libraries, gives access to complete texts within dozens of thousands of periodicals.
Student’s life
The university supports its students’ ambitions by encouraging them to pursue their interests and foster personal strengths. There are numerous student associations and academic clubs.
The University of Life Science in Lublin offers excellent sports facilities – the Sport and Recreational Centre houses a full-size sports hall, a swimming pool and aqua park, a modern gym, a dance, fitness and combat sports halls, and a climbing wall. Physical Education classes as well as University Sports Association training sessions take place there. Moreover, the university has the Didactic and Sailing Station located by Piaseczno lake close to Lublin – it disposes of cabin and Omega yachts, row-sailing boat, motorboats, and kayaks.
CONTACT
ul. Akademicka 13
20-950 Lublin
www.up.lublin.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 445 66 22, +48 (81) 533 37 52
E-mail: sekretariat.uczelni@up.lublin.
ADMISSIONS
ul. Akademicka 15, s.3 i 4
20-950 Lublin
https://www.up.lublin.pl/kandydat
Phone: +48 (81) 445 66 91, +48 (81) 445 68 85
E-mail: rekrutacja@up.lublin.pl admission@up.lublin.pl
WSEI UNIVERSITY
University of Economics and Innovation in Lublin (WSEI) was established in 2000. For almost 25 years, the university has carried out its responsibilities with great pride!
The mission
The mission of WSEI is to prepare highly qualified professionals who will be able to reinforce the human resources potential and enhance the capacity of local government institutions in terms of public finance management, strategic planning, or absorption and management of EU funds. Graduates of the university will match European standards.
In the region’s economic development, those mentioned areas of activities are the critical challenges that the public and private sectors will face in the next few years.
A diligently selected didactic staff maintains the high educational process on WSEI with proper academic degrees and necessary academic experience. A great part of the staff also has significant practical experience derived from their non-academic activity as business practitioners who are eager to share their experience gained in reputable companies and institutions.
Carrier support
WSEI offers scholarship programs, internships, or international projects.
A good organization of studies and a practical education profile make it easier for students of WSEI to combine their studies, work, and personal life. As a result, working people most often prefer to study at WSEI and non-working students do not hesitate to undertake a job while studying.
Within the framework of ERASMUS+, WSEI encourages its students to gain experience abroad as well as invites students and staff for study and training visits. More on the application
rocedures http://www.wsei.lublin.pl/wspolpraca-zagraniczna/erasmus-for-foreign-students/general-information
WSEI takes a chance to study on everybody. There are many opportunities, from the social scholarship, through the Rector’s scholarship for the best students, a special relief, a special scholarship for people with disabilities, and a minister’s scholarship for outstanding achievements.
Student’s life
WSEI has actively working scientific circles and self-government, organizing various events, concerts and social events.
The university disposes of places in a residential building with a modern design located in the center of Lublin at Unicka 3 street. The location of the student house makes it a fantastic base for exploring Lublin. You are a few-minute walk away from the campus to the Old Town, the Lublin Castle, as well as shopping malls, restaurants, clubs, bars and banks.
CONTACT
ul. Projektowa 4
20-209 Lublin
www.wsei.lublin.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 749 17 70
E-mail: bos@wsei.lublin.pl
ADMISSIONS
ul. Projektowa 4
20-209 Lublin
http://rekrutacja.wsei.lublin.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 749 32 52
E-mail: studyenglish@eiu.edu.pl
VINCENT POL UNIVERSITY IN LUBLIN
Vincent Pol University (VPU) has been created for people who want to achieve their professional goals and develop their passions. The knowledge, skills and experience gained during studying at the university enable its students to enhance their life skills and employability.
About university
The university was founded in 2000, and since then, it has been gaining worldwide popularity. Today it educates around 3000 current students, including over 40% international students, offering also on degree courses that are taught in Polish and English.
International students of VPU come from over 30 different countries. Many of them enjoy the opportunity to travel to other parts of Europe during their holidays. The university has a dedicated International Student Office that can help with applications, visas, and accommodation.
Education at VPU
Vincent Pol University is a private university approved by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education to award Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees recognized not only across the European Union but also globally.
VPU offers courses lectured in English and ELPC – English courses for non-native speakers. Students of Tourism and Hospitality Management or Sports Science at Vincent Pol University who complete their 1st and 2nd year of studies can complete their final year at the University of Bedfordshire or The University of Northampton and gain both Polish and British degree diploma.
The campus
Vincent Pol University is provided with modern buildings with special teaching rooms fully adapted to students’ needs in different classes such as physiotherapy, kinesiotherapy, cosmetology, biomechanics, massage, chemistry, tourism, hotel industry, gastronomy, geography, and IT. For maximum comfort and security, the rooms are equipped with air-conditioning and CCTV.
All the students have access to extensive libraries (with about 22 000 volumes), innovative laboratories, and free Wi-Fi connection, as well as various leisure facilities, including recreation rooms, such as gyms, fitness suites, a swimming pool, and studios for aerobics classes and other sports activities.
VPU is situated close to the city center, with easy access for students by public transport or by car. Lublin has many affordable restaurants, bars, and leisure facilities, and our students enjoy evenings out in the historic city center.
CONTACT
ul. Choiny 2,
20-816 Lublin
https://wssp.edu.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 740 72 40
E-mail: info@wssp.edu.pl
ADMISSIONS
ul. Choiny 2, Room 26
20-816 Lublin
https://wssp.edu.pl/rekrutacja
Phone: +48 (81) 448 08 20
E-mail: rekrutacja@wssp.edu.pl
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF ENTERPRISE AND ADMINISTRATION IN LUBLIN
The University College of Enterprise and Administration in Lublin (WSPA) was established in 1998 as the region’s first private higher education institution. It educates over 2000 students every year.
University’s mission
The mission of the University College of Enterprise and Administration in Lublin is to teach students to be creative, develop their careers, and help them find their place in a globalizing world. WSPA develops students’ international and intercultural competencies by creating an international environment at the university and through students and faculty’s international mobility. The University College cooperates closely with numerous European and non-European universities and colleges, associations, companies and labor market institutions.
Many opportunities
The University College of Enterprise and Administration operates based on the permission granted by the Minister of National Education and pursuant to the Higher Education Act. The diplomas signed by the university are recognized in other countries in Europe and across the world. WSPA has experience in projects financed by EU Structural Funds and Lifelong Learning Programs — Erasmus, Erasmus+, Leonardo da Vinci, and many more.
Practical education is WSPA’s strong priority (internships, placements, business and public administration partners, practitioners, faculty members). Teaching methods include study in small groups, tutorials, hands-on approach, individual and group projects, community projects. The University College offers a wide variety of opportunities for students: international short and long term mobility, Career Office, internships, work projects and placements in local and regional business partners, biannual job fairs, a business incubator for students. The school also maintains close ties with the local and regional business community.
A campus
The University College’s facilities are situated on the outskirts of Lublin, in the calm district. It disposes of a big parking area for students and lecturers and an academic library with a reach book collection. There are a few small shops as well as a shopping center close to the university’s building. It is possible to get to the campus from any part of Lublin by some convenient bus lines.
CONTACT
ul. Bursaki 12
20-150 Lublin
www.wspa.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 452 94 10
E-mail: rektorat@wspa.pl
ADMISSIONS
ul. Bursaki 12,
20-150 Lublin
https://rekrutacja.wspa.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 452 94 71
E-mail: admissions@wspa.pl
HIGHER SCHOOL OF SOCIAL SCIENCE IN lUBLI
Higher School of Social Science is one of the private higher education institutions in Lublin. It educates students in the area of social and medical science.
Localization
Facilities of the Higher School of Social Science are situated in the center of Lublin. The campus is connected to other districts of the city by convenient bus and trolleybus lines. All classes take place in one, modern building. There is a private parking area for students and lecturers.
The university’s classrooms are fully-equipped with modern devices and furniture dedicated to various courses — psychology, cosmetology, medical rescue, nursery, or dance.
Quality of teaching
A high level of education is one of the essential elements of the university’s mission. Students can rely on the high-qualified, supportive teaching staff. Small groups guarantee the personal approach of lecturers and magnificent conditions to acquire knowledge and new skills.
Courses offered by the Higher School of Social Science in Lublin are based on practical classes and led by a tutor. It is possible to choose e-learning classes what makes working and studying simultaneously easier. The university offers support to its alumni in finding practices or full-time jobs.
CONTACT
ul. Zamojska 47
20-102 Lublin
www.wsns.lublin.pl
Phone: +48 (81) 531 85 56
E-mail: info@wsns.lublin.pl
ADMISSIONS
ul. Zamojska 47, p. 200
20-102 Lublin
https://wsns.pl/rekrutacja
Phone: +48 (81) 531 85 56
E-mail: info@wsns.lublin.pl
Advantages of Lublin universities
- comprehensive and expanding didactic and scientific offer (variety of fields of study: from technical and natural sciences to humanities and arts),
- the teaching staff of the universities is highly qualified and valued. Researchers are committed to developing future scientists and help them to promote their achievements,
- opportunity to conduct research work in trans-disciplinary teams led by experts and in cooperation with esteemed national and foreign centers,
- comfortable location of the universities in the city center and within the main communication routes (there is a bus stop near the building of each university),
- an expanded and upgraded infrastructure, owing to which knowledge is acquired in a comfortable environment and with the use of high-quality, specialized equipment, software, and other research facilities,
- well-equipped amenities),
- extensive and continuously growing library collections.
In support of students’ multidirectional development, the higher education institutions provide them with opportunities to participate in exciting events and initiatives of both academic and non-academic nature. What attracts young people to Lublin’s high education institutions is the unique educational climate, valued academic staff, and the diversity of study fields: from technology and life sciences to medicine, the humanities, and arts.
Popular groups of study fields
The most popular ISCED groups studies among Polish students who started their studies in Lublin in the 2020/21 academic year are: Technology, Industry, Construction (07), Business, Administration and Law (04), Arts and Humanities (02) and Health and social care (09).
Chart 1. Polish students who started their studies in Lublin according to ISCED groups in individual academic years.
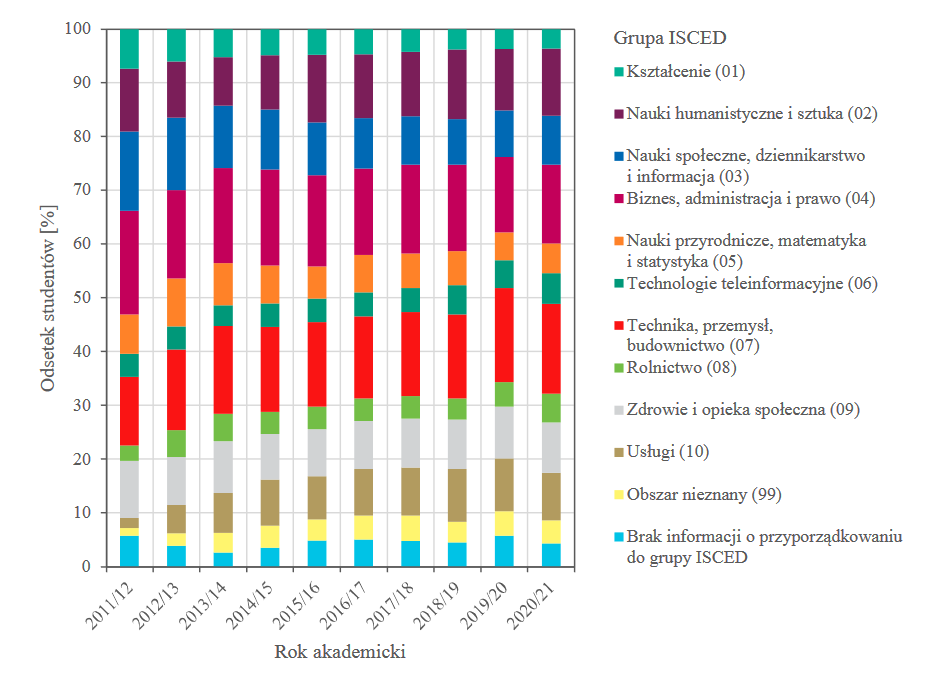
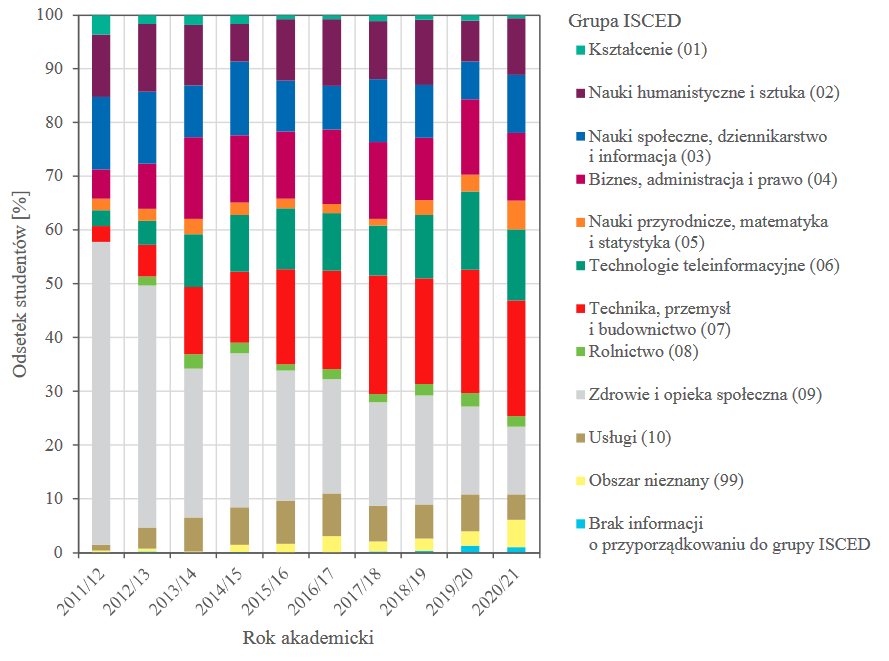
In recent years, foreign applicants for studies have been most interested in the following ISCED groups studies: Technology, Industry, Construction (07), Business, Administration and Law (04), Arts and Humanities (02) and Information and Communication Technologies (06).
Chart 2. Foreign students who started their studies in Lublin according to ISCED groups in individual academic years.
The most popular fields of study in Lublin for full-time first-cycle and unified master’s studies, according to the total number of applications submitted by candidates, based on the 2023/2024 recruitment data from www.otouczelnie, are: Medicine at UMLub, Dentistry at UMLub, Veterinary Medicine at UP, Computer Science at Pollub, Physiotherapy at UMLub, and Pharmacy at UMLub. Following these are: Nursing, Civil Engineering, Finance and Accounting, and Marketing and Market Communication.
Regarding the number of candidates per spot, the most competitive fields of study for the 2023/2024 academic year were: Dentistry at UMLub (15.27 candidates per spot), Psychology at UMCS (11.8), Medicine at UMLub (10.7), Criminology at UMCS (10.4), Veterinary Medicine at UP (9), Veterinary Analytics at UP (9), and Public Relations and Information Management at UMCS (8.75). Other popular fields included: English Studies, Management, Journalism and Social Communication, and Applied Linguistics.
Student Exchange
Depending on the school, students have different exchange opportunities. The countries involved in the partnership programs of all the Lublin-based higher education institutions are Algeria, Armenia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, China, Croatia, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Indonesia, Latvia, Moldova, Netherlands, Philippines, Portugal, Russia, Slovakia, Spain, Turkey, Ukraine, USA.
Foreign Languages
In times of dynamically changing needs of the labor market, education must be a multidisciplinary process. One of the critical features of graduates of schools of higher learning expected by employers is foreign language competence. Increasingly often, the knowledge of two or even more foreign languages is required.
Lublin’s leading schools of higher education are aware of this and are continuously expanding the range of the foreign language taught. There are now 4 to 8 different languages to choose from, with two obligatory at most universities and colleges in Lublin (only the College for Social Sciences, the University of Vincent Pol, the Medical University, and the University of Technology requiring one language). In addition to modern languages, KUL requires Greek and Latin. UMCS offers courses in Norwegian, Chinese, Portuguese, Ukrainian, and Bulgarian. English prevails at private institutions, with Spanish, German, or Russian available as options.
In addition to foreign language courses, languages can be learned in dedicated fields of study. A high standard of education in those fields is noteworthy. Each year many students in Lublin major in foreign languages. These are mainly English, German, French and Russian, but less popular languages, such as Dutch, Bulgarian or Chinese, have been attracted increasing interest.
PhD programs
All public universities and one private in Lublin offers full-time and part-time third-cycle studies. The offer of the Lublin academic centre currently includes more than 40 fields of study, the most popular of which are: humanities, veterinary, medical, law, technical, and those related to economy, business and the IT sector.
Postgraduate programs
As an intenseacademic center, Lublin is also a place where education can be continued in postgraduate courses. The most significant interest are recorded in the fields categorized under the Pedagogical, Teaching, and Medical subgroups.
It is worth noting that postgraduate studies programs enable acquiring specific competencies and additional qualifications. This form of lifelong learning is perceived as the most flexible due to its potential for adjusting to the current needs of the labor market.
Staff potential
The academic staff potential largely determines the quality of education. Lublin is an educational centre with scientific research staff representing a high standard. Their discoveries are not only known but also developed and employed by other scientists in Poland and abroad. Representatives of academic staff in Lublin may boast high scientific expertise and reputation. What is also of great importance is that they are widely known and appreciated by students as academics. According to young people, the staff at universities in Lublin is friendly and encouraging students to meet new challenges and to follow the scientific path.
Science and Business
Scientific research as well as consulting and expert activities are connected mainly with the needs of the region, and they are mostly of a general, universal nature. As a result, scientific publications, patents and protective rights are created. Many research teams closely cooperate with foreign and domestic centres (under bilateral agreements in many cases).
Universities actively support local industry innovations based on their scientific research potential. Successful cooperation between Lublin scientists and regional companies and the possibility to apply the results of their joint research in production determines the growth rate of sectors such as biotechnology, pharmacy, information technologies or advanced services.
Tightening cooperation between Lublin scientists and local companies and the possibility of applying the results of their joint research in production has a positive effect on the level of innovation and competitiveness of Lublin’s economy and determines the pace of growth in such areas as biotechnology, pharmacy, information technology, and modern services.
Research institutes and science institutions
The scientific and research potential of the City of Lublin is created not only by universities but also by research institutes, research and development units, and enterprises. Essential entities conducting R&D activities in the City of Lublin, apart from universities, include:
| Polish Academy of Sciences Branch in Lublin | https://www.pan-ol.lublin.pl/pl/ |
| The Bohdan Dobrzański Institute of Agrophysics of the Polish Academy of Sciences | https://www.ipan.lublin.pl/ |
| The Lublin Scientific Society | http://www.ltn.pollub.pl/ |
| The Institute of National Remembrance (IPN) | https://lublin.ipn.gov.pl/ |
| Witold Chodźki Institute of Rural Medicine | http://www.imw.lublin.pl/index.php/pl/ |
| Scientific Society of the Catholic University of Lublin | https://tnkul.pl/ |
| Institute of Central Europe | https://ies.lublin.pl/ |
| Lublin Science And Technology Park | https://lpnt.pl/ |
